Botany
– Meiosis & Alteration of Generations
I. Plant
Reproduction
A. Asexual- uses existing
plant parts to grow a new, genetically identical, plant.
1. Benefits –
2. Costs –
a.
This is a real threat to some of our crops like bananas.
B. Sexual-
uses _______________________ and ________________________
to produce
a new, genetically different, plant.
1. Benefits –
2. Costs –
II. Some important background information
A. What is a chromosome?
1. The information to build all living things on
earth is stored in DNA.
2. A ________________________ is a long strand
of DNA.
3. On the chromosome, you find
________________________.
a. A Gene
bears instructions for one specific trait (e.g. flower
color)
b. Where the chromosome goes, so go all of the
genes on that
chromosome.
|
Human chromosomes |
||
|
|
Female |
Male |
|
|
|
|
Image
modified from the following source: www.ucl.ac.uk/~ucbhjow/b241/genome.html
Female
chromosome source: https://blog.insito.me/the-x-in-the-sex-chromosome-d81a318533fc
Male
chromosome source: https://www.biologycorner.com/APbiology/inheritance/12-1_chromosomal_inheritance.html
B. What are homologous chromosomes?
1. Most eukaryotic organisms (those with nuclei
in their cells) are
________________________.
2. Diploid
cells have two sets of chromosomes.
a. One set of chromosomes is
________________________
(inherited
from the mother),
b. One set of chromosomes is
________________________
(inherited
from the father).
c. We denote a diploid cell as
________________________.
3. ________________________ chromosomes – chromosomes of the
same
length, same centromere position, and that carry genes for the
same
traits.
a. One member of the homologous pair you
inherited from your
mother.
b. The other member of the pair you inherited
from your father.
C. Consider human sexual reproduction (since
we’re all somewhat familiar with
that)
1. Humans have 46 chromosomes (or 23 pairs of
chromosomes)
a. 23 of these chromosomes are maternal
b. 23 are paternal
c. These chromosomes are numbered 1 through 23
(with the 23rd
pair
being the sex chromosomes X & Y)
2. Russell, my husband, and I have successfully
reproduced. We had the
world’s
cutest and sweetest little boy, Nathan.
a. If
Russell had passed on all 46 of his chromosomes, and I had
passed on all 46 of my chromosomes
to Nathan, how many
chromosomes would Nathan have
ended up with?
b. The answer is ________________________! No human has
ever survived a birth defect
this catastrophic.
3. So, sexually reproducing organisms DON’T pass
on all of their
chromosomes to their
offspring.
a. When we make sex cells, we do so through a
special process
known as
________________________.
b. When a cell enters into meiosis, it is
diploid (or 2n).
Remember, this means it has
homologous (maternal & paternal)
pairs of each of its
chromosomes.
c. During meiosis, only one member of each
homologous pair is
incorporated into the sex
cell or ________________________.
d. These resulting gametes are
________________________ or
________________________. They have either the maternal or
the paternal copy of each of
your chromosomes, but NOT both.
4. When fertilization occurs, the sperm carries
one set of
chromosomes
to the egg. This restores the two set or
diploid
condition
and a unique individual is created.
III. ________________________- two complete cellular divisions in
which the genes on
chromosomes are shuffled and the chromosome number is
halved.
A. Meiosis consists of two successive rounds of
cell division called meiosis I and
meiosis II.
1. Each round of cell division is subdivided
into stages of …
a. ________________________
b. ________________________
c. ________________________
d. ________________________
2. Meiosis
I is known as ________________________
Division because
this is when the chromosome
number is halved. (Again, I’m going to
use
human cells as an example.)
a. What we start
with…
1) One Parent Cell (or primary sex cell)
2) This cell is diploid or 2n
3) This cell has homologous pairs of chromosomes
b. What we end up with…
1) Two secondary sex cells
2) Both of these cells are haploid or n
3) These cells have single (unpaired)
chromosomes
c. In humans…
1) We start with a primary sex cell that has 46
chromosomes
(23 homologous pairs) and is diploid or 2n
(just
like all of our other body (somatic) cells).
2) We end up with 2 secondary sex cells that
have 23
chromosomes
(no pairs) and are haploid or n.
a)
For each chromosome pair, these cells receive
either
our maternal or our paternal chromosome, but
NOT
both.
3. Meiosis
II is known as ________________________
Division. We
start
& end with cells that have the same number of chromosomes.
a. What we start
with…
1) 2 secondary sex cells
2) These cells are haploid or n (& were produced during
meiosis
I)
3) These cells have single (unpaired)
chromosomes
b. What we end up with…
1) 4 Gametes or sex cells
2 These cells are haploid or n
3) These cells have single (unpaired)
chromosomes
c. In humans…
1) We start with 2 secondary sex cells that have
23
chromosomes
(no homologous pairs) and are haploid or n
2) We end up with 4 gametes or sex cells that
have 23
chromosomes
(no pairs) and are haploid or n.
a)
For each chromosome pair, our gametes receive
either
our maternal or our paternal chromosome, but
NOT
both.
B. The phases of meiosis
**Be sure to
review the diagrams of the phases of meiosis in your textbook!**
1. ________________________ – Although the cell
is not dividing
during interphase, something
VERY important happens. The
chromosomes ________________________.
a. The parts of a replicated chromosome are…
1) ________________________– the identical
strands of
DNA
2) ________________________ – structure that
holds the
sister
chromatids together
3) ________________________ – structures that
develop
on
the sides of a centromere during late prophase.
a) The spindle fibers attach at this point of
the
chromosome
b. The DNA is still in the form of chromatin
& cannot be seen
2. Meiosis
I (or reductional division)
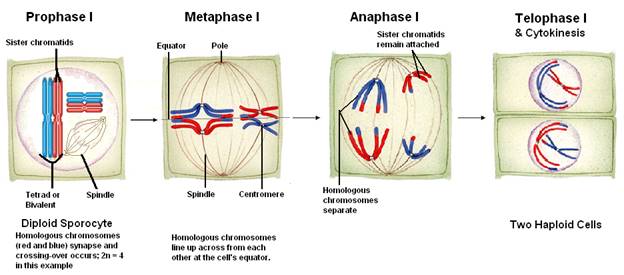
a. Prophase
I
1) Chromatin condenses into ______________________
2) The nuclear envelope dissipates.
3) The ________________________ begins to
develop
4) ________________________ occurs.
a) Synapsis is an attraction between homologous
chromosomes. They join, side by side.
b) These synapsed homologous chromosomes are
called
________________________ or
________________________.
5) When homologous chromosomes are synapsed,
they
often exchange like portions
of their chromatids, a process
called
______________________________________________.
a) The points where crossing over occurs are
called
________________________.
b) This occurs frequently, e.g. it's been
estimated
that each pair of human
chromosomes undergoes 2-
3 crossing over events during
every prophase I of
meiosis.
c) This is one of the greatest sources of genetic
________________________. What we pass on is
a unique chromosome, not
exactly our mother’s
chromosome or our father’s
chromosome, but an
unique combination of the two.
|
|
Electron Microscope View of Chiasmata
|
b. Metaphase I
1) The synapsed chromosomes separate.
2) The homologous chromosome pairs align across
from
each
other at the ________________________.
a) The way in which parental chromosomes are
arranged at the metaphase
plate is random and the
number of possibilities of
their organization is 2 to
the power of the number of
chromosomes
b) In humans there are 2 to the power of 23
possible arrangements of
human chromosomes (i.e.
only 1 in 8,388,608
possibilities that two eggs or
sperm will receive an exact
maternal or paternal
complement of chromosomes.)
c. Anaphase
I
1) The homologous chromosome pairs are pulled by
their
__________________________________________away
from
each other, toward opposite poles of the cell.
2) ___________________________________________
are
broken.
d. Telophase
I
1) The chromosomes reach opposite poles.
2) The spindle begins to break up.
e. ________________________ separates the
chromosomes into
two
cells, each of which now has half of the number of
chromosomes
that were found in the parent cell. In
other words,
the
cells are now haploid.
3. Meiosis
II (or equational division) – if you remember what happened
in mitosis from the chapter on cells, then you
already know what we’re
about
to go over.
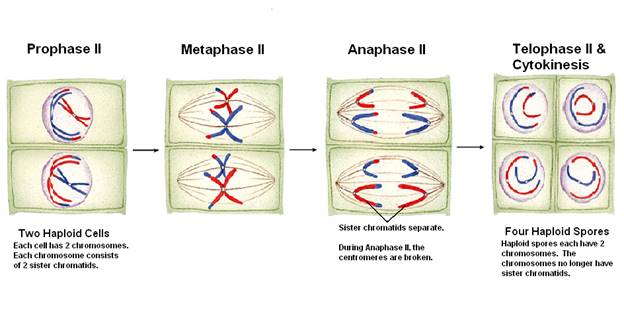
a. Prophase
II
1) A short Interphase may occur between
Telophase I and
Prophase
II.
a) Each of the secondary sex cells usually stays
in
prophase II without
reformation of the nuclear
envelope.
b) No DNA replication occurs.
2) The spindles begin to develop.
b. Metaphase
II
1) The chromosomes line up at the cells equator
2) Spindle fibers are attached to each chromatid
c. Anaphase
II
1) The centromeres are broken as the spindle
fibers pull
the
sister chromatids toward opposite poles.
d. Telophase
II
1) Sister chromatids reach opposite poles &
begin to
Uncoil
& return to being chromatin.
2) Nuclear envelopes form.
3) Spindle begins to break up.
f. Cytokinesis
takes place
1) New cells are
haploid.
2) 2 cells form
from each haploid cell produced in
meiosis
I.
3) A combination
of meiosis I and II therefore produces 4
haploid
(n) cells from one diploid (2n) cell.
IV.
Fertilization and the alternation of generations
A. In animals, sexual reproduction is
accomplished through the union of gametes
to form a zygote.
B. In plants, the process is more complicated
with two possible organisms
formed.
1.
________________________-
a. The suffix phyte means
“________________________”. The
sporophyte is the generation
of the plant that produces the haploid
________________________ by
________________________.
b. The spores germinate to form a haploid
gametophyte.
2.
________________________-
a. The gametophyte is the generation of the
plant that produces the
________________________
(eggs & sperm) by
________________________.
b. The gametes fuse through
________________________ to
form
the ________________________, which develops into the
________________________.
C. In very primitive plants,
the gametophyte is dominant.
D. In vascular plants, the sporophyte is
dominant.
E. Fungi and some algae also have alteration of
generations in which the
gametophyte is usually
dominant.
V. A Typical Life Cycle of Plants that Undergo
Sexual Reproduction
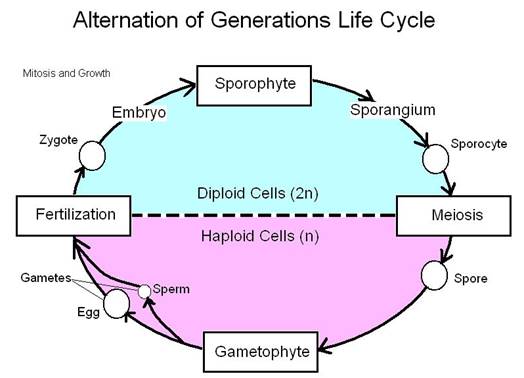
Image by Scarlet Estlack.




